The rhizome of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC., Shegan, is a traditional Chinese medicine conventionally used for the treatment of a sore swollen throat, asthma, phlegm expelling, tonsillitis, and many other symptoms. Phytochemical studies of B. chinensis conducted to date have revealed the presence of isoflavonoids and iridal-type triterpenoids.
Isoflavonoids are considered to be the major constituents of rhizoma Belamcandae and are generally regarded as the index for quality assessment of this herb and responsible for its estrogenic and anti-inflammatory effects.
The presence of a number of iridal-type triterpenoids, which exhibited a variety of biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, PKC activation, RasGRP pathway modulation, and ichthyotoxicity, have been reported in B. chinensis.
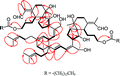
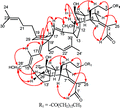
The apparent rich chemical diversity of B. chinensis and various biological activities of iridal triterpenoids prompted us to scale-up the study of this plant, affording a novel dimeric triterpenoid, dibelamcandal A, possessing a six-membered ring linking two iridal-type triterpenoid nuclei.
Chengdu Institute of Biology DING Lisheng's team describe the isolation, structure elucidation, and toxicity evaluation against Pomacea canaliculata.