Among the three divisions of algae (Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta and Rhodophyta), the member of Chlorophyta is less intensively studied.
The marine green genus Codium has been found to be an important source of clerosterol, and its oxygenated derivatives.
Several reports mention that some oxygenated sterols possess interesting biological activities. C. divaricatum Holmes, in China, is eaten as food by some of the people along the coastlines and is used as a traditional Chinese medicine for an anticancer and anthelmintic agent, detoxification, and detumescence. This is the first report of a chemical investigation of C. divaricatum.
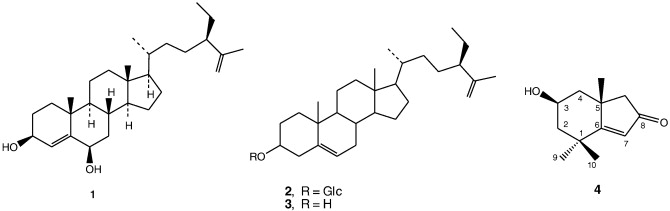
In the present study, Chengdu Institute of Biology Dr.HE Zhizhou and her colleagues have isolated a new sterol, 24-R-stigmasta-4,25-diene-3β,6β-diol , along with three known compounds (2–3) from the green alga Codium divaricatum Holmes, a traditional Chinese medicine, which is efficacious against cancer.
However, all structures were determined by spectroscopic methods and comparison with related known compounds. Single-crystal X-ray crystallography allowed us to confirm the structure of 1.
Then, it is concluded that the compound 1 is reported as the first from natural source, and compounds 2, 4 have not been isolated from green algae before. More results have been published in FITOTERAPIA in Dec.2010.
Graphical Explanation: A new sterol 24-R-stigmasta-4, 25-diene-3β, 6β-diol (1), along with a sterol glycoside 24-R-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-stigmasta-5, 25-diene (2), clerosterol (3), and loliolide (4) was isolated from the green alga Codium divaricatum Holmes.